In recent years, the field of healthcare has witnessed an incredible transformation thanks to advancements in robotics and artificial intelligence (AI). Robots, once confined to factories and assembly lines, are now making their way into hospitals and operating rooms, offering a level of precision, efficiency, and reliability that is changing the way we think about surgery and medical care. Today, robots are not just assistants; they are becoming vital members of medical teams, helping doctors perform surgeries, diagnose conditions, and improve patient outcomes.
A New Era in Surgery: Robotic-Assisted Operations
One of the most exciting developments in healthcare robotics is the rise of robotic-assisted surgery. Robots are now playing a crucial role in performing minimally invasive surgeries with a level of accuracy and dexterity that human hands alone could not achieve. Using state-of-the-art technology, robots can perform complex procedures through tiny incisions, which offers patients several benefits, including shorter recovery times, reduced pain, and minimal scarring.
The most well-known example of a robotic surgical system is the da Vinci Surgical System, which allows surgeons to control robotic arms with precision from a console. This system provides high-definition 3D visualization, enhanced flexibility, and fine motor skills that surpass human capabilities. Surgeons can manipulate the robotic arms in ways that would be impossible using traditional tools, improving both the speed and success rate of surgeries.
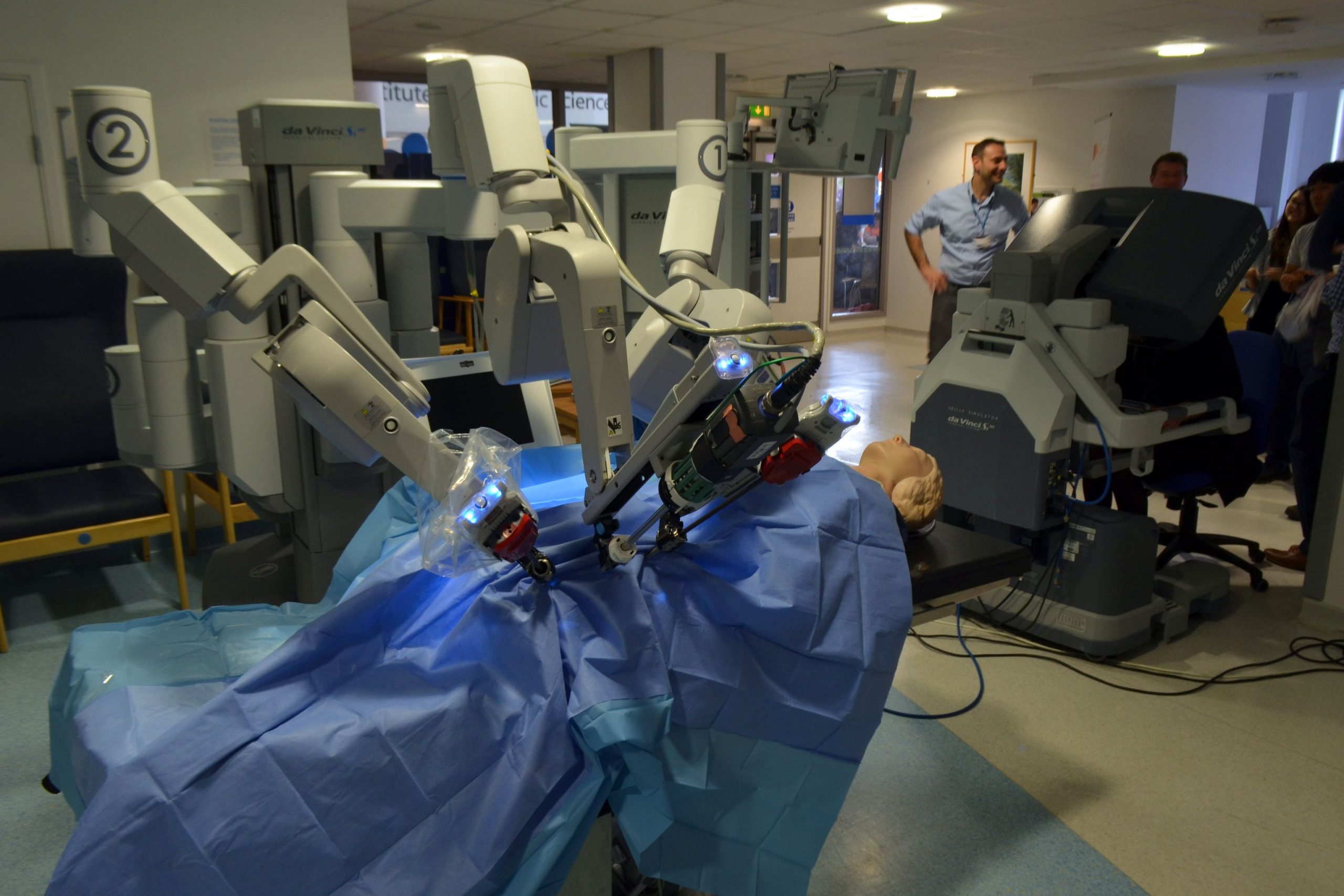
How Robotic Surgery Works
Robotic surgery typically involves several key components:
- Robotic Arms: These arms are equipped with surgical instruments and can perform delicate procedures with great precision.
- Console: The surgeon sits at a console, controlling the robot’s movements in real-time. The console offers enhanced visualization of the surgical site, often with 3D images, providing better depth perception and clarity.
- Camera and Sensors: High-definition cameras and sensors provide real-time data and imagery, allowing the surgeon to make informed decisions during the procedure.
Benefits of Robotic Surgery
The integration of robots in surgery offers numerous advantages, both for patients and medical professionals:
- Minimally Invasive: Robotic systems allow for smaller incisions, which leads to reduced blood loss, less tissue damage, and a faster recovery time. Patients often experience less pain and can return to their normal activities sooner.
- Increased Precision: Robots can perform movements with extraordinary accuracy, reducing the risk of human error and enhancing the success rate of surgeries.
- Better Visualization: The high-definition cameras used in robotic systems provide surgeons with a clearer, magnified view of the surgical area, helping them make better decisions.
- Enhanced Dexterity: The robotic arms can maneuver with greater precision than the human hand, making complex procedures more manageable.
- Shorter Recovery Times: Thanks to the minimally invasive nature of robotic surgeries, patients can recover much faster compared to traditional open surgeries.
Robots Helping Doctors in Diagnosis and Treatment
Beyond surgery, robots and AI are also playing an increasing role in diagnosing diseases, providing treatment recommendations, and assisting in patient care. AI-driven algorithms can analyze vast amounts of medical data—such as imaging scans, lab results, and patient histories—much faster and more accurately than human doctors alone.
For example, robotic imaging systems can detect early signs of diseases like cancer, cardiovascular issues, and neurological disorders, providing more accurate diagnoses. The AI algorithms behind these systems can analyze scans, identify patterns, and even detect minute changes in tissues that might be missed by human eyes.
In addition, robots are being used to support doctors in clinical settings. For instance, telepresence robots allow doctors to interact with patients remotely, providing consultations and follow-up care. These robots can also be used in underserved or rural areas, where medical specialists might not be readily available.
The Role of Robots in Rehabilitation
Robots are also making a significant impact in rehabilitation therapy. Robotic exoskeletons are being used to assist patients with mobility impairments, helping them regain the ability to walk or perform other physical activities. These exoskeletons are controlled by the patient or a therapist and are designed to assist with movement while also providing feedback to the patient’s muscles and joints. The technology is especially beneficial for individuals recovering from spinal cord injuries, strokes, or other neurological conditions.
The Future of Healthcare Robotics
While robots are already making an impact in healthcare, the future holds even more exciting possibilities. Researchers are continuously developing new technologies that will make robots even more autonomous, efficient, and capable. AI-powered robots are expected to take on an increasing role in providing personalized care, predicting medical conditions before they become critical, and even carrying out entire surgeries with minimal human intervention.
In the coming years, we may see more robots in the form of surgical assistants, diagnostic tools, and even personal care companions for patients. The integration of 5G networks and advanced AI will further enhance the capabilities of healthcare robots, allowing them to make faster, more informed decisions and work in tandem with human doctors.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges
Despite the tremendous potential of healthcare robots, there are challenges and ethical considerations to address. One of the main concerns is the role of human oversight—how much control should robots have over medical decisions, and what happens if something goes wrong? Ensuring that robots assist, rather than replace, healthcare professionals is a critical issue that must be addressed as the technology evolves.
There are also concerns about data security. With robots collecting and analyzing vast amounts of patient data, ensuring that this information is protected from breaches and misuse is paramount. Healthcare providers will need to establish robust cybersecurity measures to safeguard patient privacy.
Conclusion
The integration of robots into healthcare is not just a trend but a profound transformation that is reshaping the medical field. From performing high-precision surgeries to assisting in diagnosis and rehabilitation, robots are becoming invaluable tools in improving patient care and outcomes. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect robots to play an even greater role in revolutionizing healthcare, making medical services faster, safer, and more accessible than ever before.
The future of healthcare is undoubtedly robotic, and it is a future that promises to enhance the lives of both doctors and patients alike.